The Economics of Intrigue: The Way Dark Web Markets Operate
The digital age brings forth a multitude of new markets, but none are as puzzling and debated as the dark web markets. Concealed from the prying eyes of conventional browsing, these sites thrive in the shadows of the internet, often conducting business that challenges lawful and moral boundaries. Digital currencies like Bitcoin have given cloak and dagger operations the means to flourish, allowing users to buy and sell everything from artwork to illegal substances with a level of discretion that traditional markets do not possess.
Surfing the dark web is not for the faint of heart. The hidden internet, as it is commonly called, requires distinct software to access, and even so, it poses many risks, including scams and law issues. The fascination of these secret platforms lies not just in the accessibility of hard-to-find items but also in the feeling of camaraderie they cultivate among users who share a suspicion of the conventional internet. This piece delves into the complex workings of dark web markets, looking into how they operate, the culture that envelops them, and the consequences for those who choose to participate in this covert economy.
Comprehending the Obscure Web
The dark web refers to a section of the internet that is not at all indexed by conventional search engines, which makes it accessible only through particular software and settings. Generally, users connect to it via the Tor network, which conceals their online actions and allows for both privacy and, in numerous instances, illicit behaviors. This covert space hosts a plethora of marketplaces, forums, and communication platforms that enable various activities, both legal and illegal.
One of the most striking aspects of the shadow web is its use for private transactions. Users often participate in the buying and selling of goods and services that are difficult or not feasible to find on the surface web, including controlled substances, arms, hacked information, and fake money. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are frequently utilized in these transactions to enhance anonymity, offering a layer of protection for both purchasers and sellers. This financial aspect has led to a complicated ecosystem where trust and reputation play key roles in market dynamics.
While the dark web is often associated with illegal activities, it is also a space for free expression, particularly in regions where censorship is prevalent. Advocates, journalists, and whistleblowers frequently use dark web tools to connect safely and share information without worry of retribution. This duality underscores the dark web's multifaceted nature, existing as a sanctuary for certain freedoms while concurrently being a platform for nefarious dealings.
The Economics of Darknet Markets
Darknet markets operate within a distinct financial structure that contrasts sharply with traditional marketplaces. Such platforms primarily thrive on anonymity, facilitated by technologies like the Tor network that obscure user identities and locations. The need for confidentiality often arises due to the illicit nature of many goods and services exchanged, such as drugs, weapons, and hacked information. This environment creates a market driven by demand where sellers can set prices based on the assumed risk associated with their products and the anonymity of their buyers.
The competitive landscape in these markets is shaped by a diverse range of vendors, each attempting to capture buyers' attention through feedback, quality of goods, and pricing strategies. Vendors often use escrow services to instill trust among buyers despite the intrinsic uncertainties of online deals. Additionally, cryptocurrencies play a crucial role in the dark web, as they offer an additional layer of anonymity and security, which enhances sales and transactions outside of conventional banking systems.
Despite their illicit nature, darknet markets exhibit traits resembling permitted markets, including supply and demand dynamics, marketing strategies, and customer service practices. Some vendors allocate resources in sophisticated logistics to ensure timely delivery of products, while others focus on cultivating trust through consistent positive interactions with buyers. Overall, the economics of these marketplaces demonstrate a intricate balance of anonymity, risk, and competition that shapes how they function and evolve.
Risks and Legal Implications
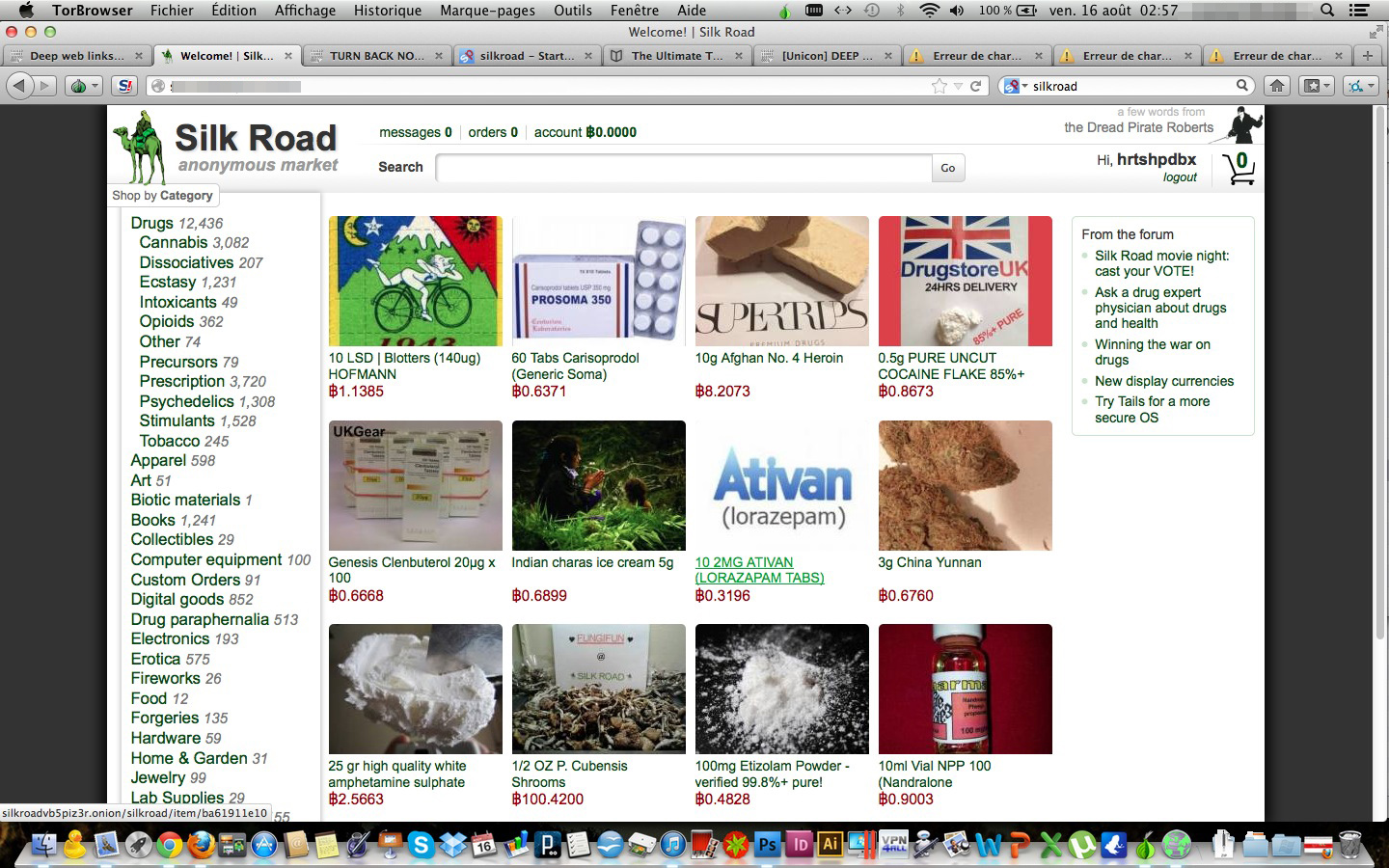
Involvement with dark web markets carries significant hazards for individuals. Consumers may encounter scams, resulting in fake goods or no products at all after payment is made. Furthermore, personal data can be vulnerable to malicious actors, resulting to identity theft or monetary fraud. The anonymity that dark web markets offer can easily be breached, putting users at danger. darknet markets onion
The legal implications of involvement in these markets can be serious. Many goods and services traded on the darknet, such as illicit drugs, weapons, and stolen data, are banned by law. Law enforcement agencies actively monitor these platforms, employing sophisticated techniques to identify users. Individuals caught buying or selling prohibited items can face heavy fines and criminal charges, with potential prison sentences depending on the seriousness of the offense.
Additionally, even if a person does not participate in illegal activities directly, merely visiting dark web markets can lead to unwanted legal scrutiny. In many jurisdictions, this can create suspicion and result in investigations. Therefore, the potential consequences of exploring these markets extend further than the direct actions taken, affecting ongoing personal and professional lives.